Instead the system might get stuck in some local minimum of the Gibbs potential. We can measure only changes in free energy.
13 7 The Gibbs Free Energy Chemistry Libretexts
Use the information in Appendix G to estimate the boiling point of water.
. The appellation free energy for G has led to so much confusion that many scientists now refer to it simply as the Gibbs energy. The standard free-energy change ΔG is the change in free energy when one substance or a set of substances in their standard states is converted to one or more other substances. Free energy has the dimensions of energy and its value is determined by the state of the system and not by its history.
In more fundamental terms 1 joule is equal to. At constant temperature the Helmholtz free energy is minimized at equilibrium. The default tolerance is usually very small of order 1e-15.
Matlab uses a tolerance to determine what is equal to zero. It is expressed in two forms. Gibbs Free Energy is the thermodynamic quantity of a system that is the energy available to do work.
Concepts of work kinetic energy and potential energy are discussed. If the absolute value of a number is less than 1e-5 you may consider that close enough to be zero. Gº is zero then the value of the equilibrium constant K will equal to.
If there is uncertainty in the numbers you may have to define what zero is eg. Free energy is used to determine how systems change and how much work they can produce. ΔG is the maximum amount of energy which can be freed from the system to perform useful work.
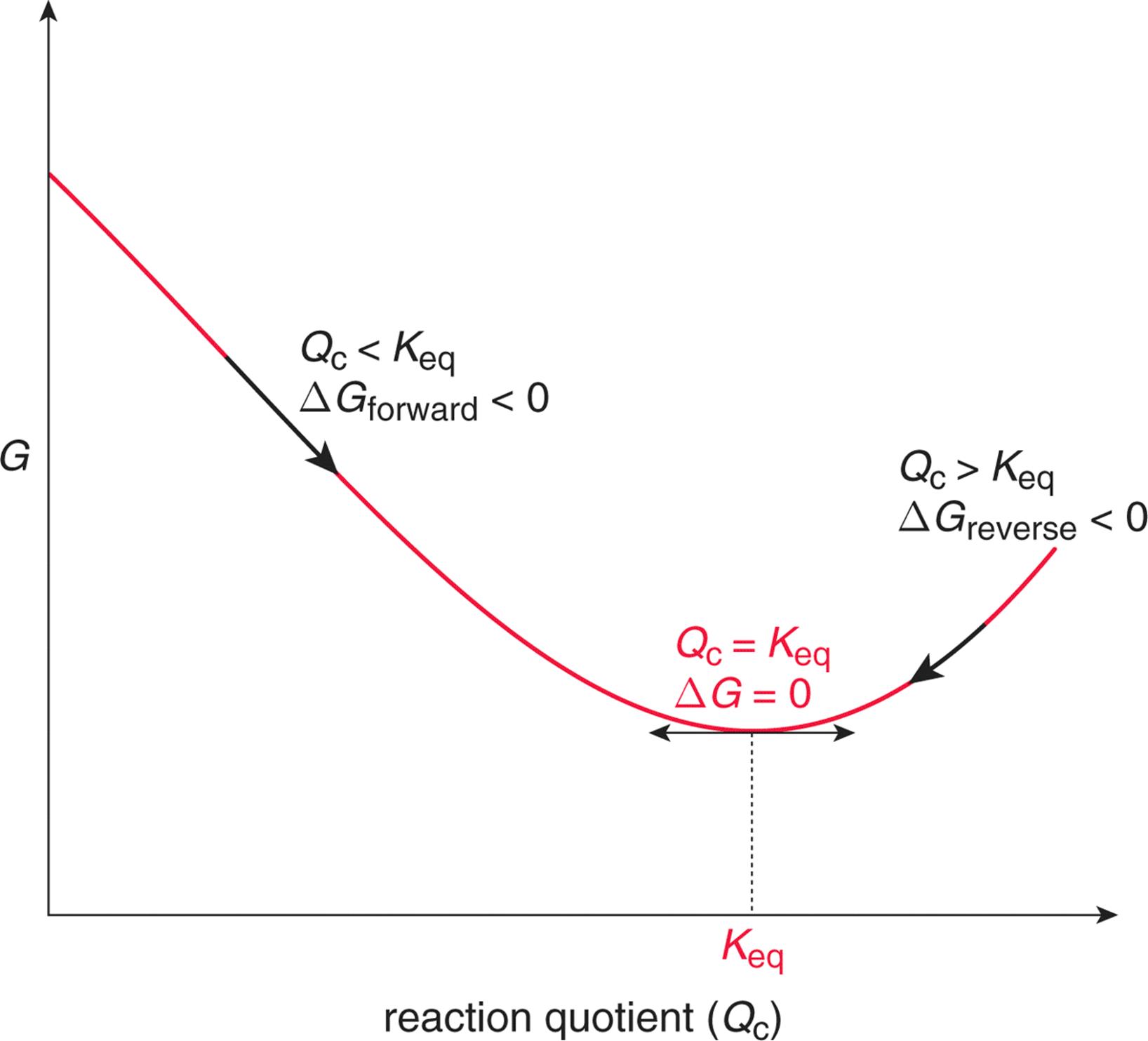
E sys q v. Δ f G Δ f G RT ln Q f where Q f is the reaction quotient. However if some systems variable changes other parameters might not necessarily adapt to these changes and the system might not always immediately assume the point of lowest possible Gibbs free energy.
Its value is usually expressed in Joules or Kilojoules. At equilibrium Δ f G 0 and Q f K so the equation becomes Δ f G RT ln K where K is the. For an equilibrium reaction if the value of standard Gibbs free energy.
The free part of the older name reflects the steam-engine origins of thermodynamics with its interest in converting heat into work. The Gibbs free energy G is equal to the work exchanged by the system with its surroundings when a system changes from an initial state to a final state minus the work of the pressure force. For detailed discussions on the spontaneity of a process on the basis of Gibbs free energy change check out BYJUS -The Learning App.
What I mean by naturally is that a reaction will occur in a system without the net influx of free. This new property is called the Gibbs free energy G. H 2 O l H 2 O g H 2 O l H 2 O g When this process is at.
In contrast the Gibbs free energy or free enthalpy is most commonly used as a measure of thermodynamic. If we believe that any number less than 1e-5 is practically equivalent to zero we can use. Two phases in equilibrium under such conditions have equal Gibbs free energy.
The relationship between the change in the internal energy of the system during a chemical reaction and the enthalpy of reaction can be summarized as follows. Gibbs free energy is denoted by the symbol G. Gibbs free energy also known as the Gibbs function Gibbs energy or free enthalpy is a quantity that is used to measure the maximum amount of work done in a thermodynamic system when the temperature and pressure are kept constant.
Gibbs free energy can be defined as the. Simply put spontaneous processes are those that occur naturally and nonspontaneous processes are those that do not. The heat given off or absorbed when a reaction is run at constant volume is equal to the change in the internal energy of the system.
Free energy in thermodynamics energy-like property or state function of a system in thermodynamic equilibrium. At which its liquid and gaseous phases are in equilibrium that is when vaporization and condensation occur at equal rates. This definition causes the SI unit for energy is the same as the unit of work the joule JJoule is a derived unit of energy and it is named in honor of James Prescott Joule and his experiments on the mechanical equivalent of heat.
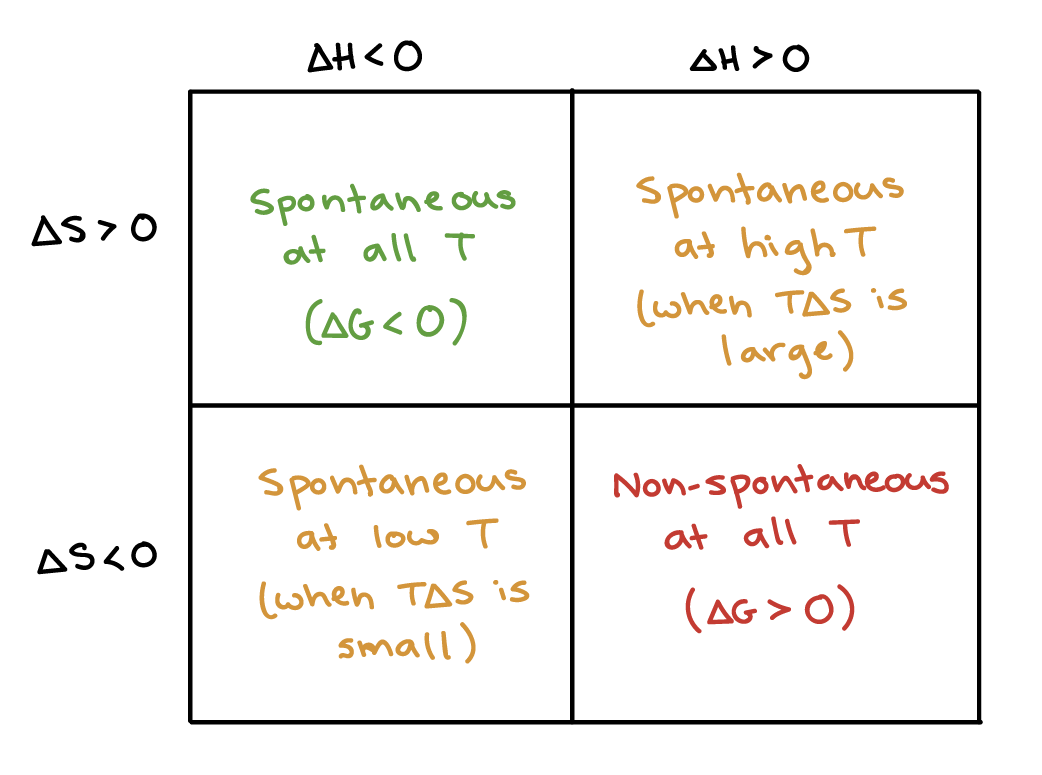
The change in the Helmholtz energy during a process is equal to the maximum amount of work that the system can perform in a thermodynamic process in which temperature is held constant. G H - TS. G.
The Gibbs free energy of the system is a state function because it is defined in terms of thermodynamic properties that are state functions. Because enthalpy is one of the components of Gibbs free energy we are consequently unable to measure absolute free energies. These concepts are combined with the work-energy theorem to provide a convenient means of analyzing an object or system of objects moving between an initial and final state.
Solution The process of interest is the following phase change. The Gibbs free energy of a system at any moment in time is defined as the enthalpy of the system minus the product of the temperature times the entropy of the system. All elements in their standard states diatomic oxygen gas graphite etc have standard Gibbs free energy change of formation equal to zero as there is no change involved.
Energy is generally defined as the potential to do work or produce heat. The change in the Gibbs free energy of the system that. It is used to determine whether or not a reaction is spontaneous.
Enthalpy Entropy And Gibbs Free Energy Equilibrium Thermodynamics
Gibbs Free Energy And Spontaneity Article Khan Academy

Gibbs Free Energy Thermochemistry Training Mcat General Chemistry Review
0 Comments